An Introduction to Supply and Demand in Forex
What is Forex?
Foreign currency (also known as Forex or FX) refers to the global, over-the-counter market (OTC) where traders, investors, institutions, and banks buy and sell currencies.
Trading is conducted on the “Interbank Market,” an online channel through which currencies are traded 24 hours, five days a week. With a global daily volume of over $5 trillion, forex is the largest financial market.
All transactions on the foreign exchange merchandise involve simultaneous buying and selling of two currencies.
The trade supply and demand sectors are observable areas on a foreign exchange chart where price levels have moved several times in the past. Unlike the lines of support and resistance, these are more closely similar to the exact lines.
Traders can customize the chart to identify the trading supply or demand zone shown on USD/JPY below:
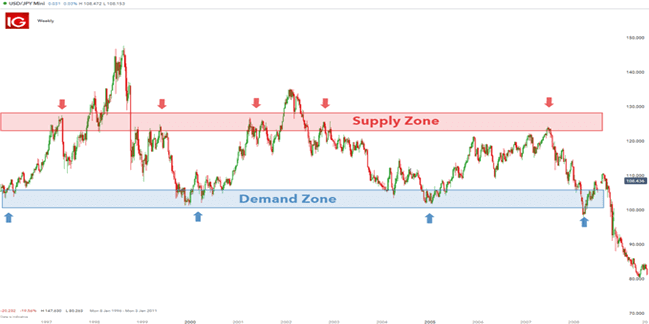 Supply and Demand in Forex Trading
Supply and Demand in Forex Trading
Supply or demand trading in Forex is a trading style where the idea is to find those turning points in the market where the price has made a strong advance or decline and characterize these trading areas as supply or demand areas that are using rectangles. The point at which the price has made a substantial advance is marked by the trading as a demand zone. A point where there is a sharp decline in the merchandise is marked as a supply zone.
Supply and demand Forex trading strategies are the mainstays of business when the market speeds up or decreases, large institutions, i.e., banks/hedge funds, are not able to bring their entire business to market, so they leave pending orders to buying and selling. With the expectation that the supply-demand zones would return to the area and fill its remaining trading positions.
For retail traders or forex market traders who don’t know much about supply and demand trading, the theory already mentioned seems to make sense. The problem is that the above principle is completely wrong in the way the forex trading supply and demand merchandise works. Forex traders with 90% supply zone and all trade demand supply and demand zones with the idea that large institutions are ready for pending orders on these zones when the merchandise returns, it is wrong! Institutions never do anything like this, and even if they have placed a forex market order on the supply and demand zone when the market will affect this order, it will not go anywhere because unfilled orders cannot cause the market price returns to change, only the merchandise can only order.
Supply zones refer to the number of available goods during demand, the quantity of an asset that people who have buying interest. As the supply level of goods increases, its price levels decrease. Conversely, as the supply of an asset decreases, its price level increases. As the demand level for goods increases, its value increases. Conversely, as the demand levels for an asset decreases, its value decreases. As this principle applies to the money merchandise, many traders look at the supply and demand level for a particular currency over time to determine whether the currency’s value will increase or decrease.
One way to measure the trading supply or demand zone is to give a watch view picture with all the fundamental factors influencing that currency. For example, in an economic report, when supply or demand increases or decreases respectively for the US dollar, but that basic factor to the left of the lead. When financial or calendar events either reduce demand levels for the US dollar or increase supply, the place that is the fundamental factor to the lead’s right. If you need to open an account, you need to sign up with your name, email, and email address. If there are more factors to the left, then the CISO will tilt upward, and the value of the US dollar should rise. On the other hand, if there are more factors to the right, the CISO will tilt downward, and the value of the US dollar should fall.
In this way, trading for forex traders can pay attention to all the recent important factors that are affecting a particular currency. This is helpful in evaluating whether this currency is performing relatively well.
How Do Supply and Demand Forex Trading Work?
Trading Supply and demand within simple vegetable merchandise are not all that much different from what happens every day in the foreign exchange merchandise. In some cases, these forces are moving at such high probability trades speeds that new traders may have difficulty understanding the nuances of details.
The forex trading merchandise is the largest financial merchandise in the world due to the massive demand level behind traded assets. Currencies are the basis of the world’s economy, and whenever an economy wants to trade with another economy (provided different currencies are used), the exchange will be required.
In short, trade Forex supply and demand work by analyzing the volume of buyers and sellers within the foreign exchange merchandise.
Imagine that the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) makes an interest rate change. A full chain reaction will be set in motion due to the forces of supply and demand. When rates rise, foreign exchange rollover payments also increase.
This means that investors who are making open trade at specified rollover times (vary from country to country) will receive a higher interest rate than before – the incentive has just increased.
All else being equal, more merchants will want to buy; And fewer merchants wish to sell as a sales opportunity cost (rollover payment) has become more expensive.
Supply and demand forex – USD/ZAR daily price chart:
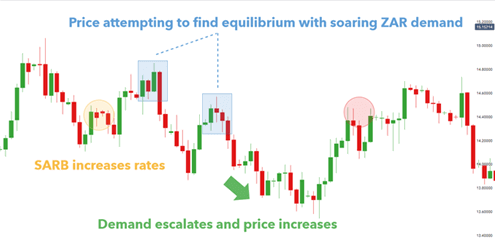
As you can see, the price aims to find comfortable turning points and will increase until a buyer is ready to pay that price. At this point, sellers kill buyers, and the price breaks down and responds.
After a significant decrease in value (red circle), the merchant will return to the picture, recalling the increased interest rate and additional rollover payments receiving a more extended rollover price range. In this way, a lower price presents a ‘perceived value.’
All traders for trading experience in this merchandise are sitting on paper profits only and have not made a real profit until they sell, so there are a ton of potential orders in this merchandise that want to sell to realize profits, all not to mention others, who have only entered near the top with other traders, are still accumulating in long trades, with the uptrend trying to hold their stock. Once some traders start taking profits at a higher level, this market may begin to reverse lower.
It is the process of finding its fair value because it occurs in many different time frames in every merchandise in the world.
The relationship between the supply zone and demand zone, along with the support and resistance levels of an asset, is important. This is because when the price crosses the key support and resistance levels, there can be a change in supply and demand zones within that currency pair.
So What Really is Supply and Demand Zones in Forex?
The supply of this economics, the quantity of a commodity that is to enter the market, and available for purchase or available for purchase at a particular price moves.
Demand, coupled with this economics, willingness to buy, the power to do so. The number of goods that the buyer will take at a particular amount.
In more basic terms, supply is the quantity of something that merchandise has and is freely available to buy in the selling area, and the demand is just how much the merchandise wants to buy.
Supply and demand is a powerful force, and it is a lot of work around us than the price we pay for our milk, how much we pay for our apples in the supermarket and that is why governments are so strict on ensuring in all regions and a large company, competition does not take place on a single product and is then able to control all supply and demand level, and control all price range.
Analysis of Supply and Demand in Foreign Currency Pairs
A supply and demand-based trading system is a relatively simple yet powerful way to trade Forex. The rules for supply and demand analysis in forex are quite simple. When the price action reaches a demand level and bounces upwards, we should buy. We expect the price to increase as a result of total buy orders in the demand area. Therefore, we have the opportunity to ride the upcoming amount of swing.
In the opposite direction, when the price reaches a supply level and bounces down or trades in a consolidation zone, we should sell. You assume that the price action will start triggering sales orders collected in that area, which is likely to cause a price drop. In this way, it creates an opportunity to ride a bearish move on the chart.
When they are tall in the merchandise, we place a stop-loss order just below the demand zone. Conversely, place our stop loss order just above the supply area.
The most common approach is to hold our trades until the price will go to the opposite level on the chart. Therefore, if we have been trading at the level of demand for a long time, then we should hold your business until the price supply on the chart reaches the next supply area. Conversely, if we are lowering the supply level, we should hold our business until the next demand level comes to the price graph.
Many times, however, there is no clear level to target, or it may be far away. Often the price may not be able to reach the opposite level during its move. Therefore, they suggest that when we set our exit point on the chart, they also use simple price action derivative analysis. To do this, they can use various push the price range clues such as Trend, Channel or Swing Top, and Bottom Analysis.
How to Find Supply and Demand Area on the Chart?
Then the obvious question becomes: “How do I find the supply and demand sectors on the chart?” Identifying supply and demand zones is quite simple once you know what to look for. First, zoom out your trading time frame chart and switch to the next higher level time frame. The next level time frame is 4x or 5x your trading time frame. By doing this, you will have a bird’s eye on the overall price action.
Then see a twist in price action where prices have reacted rapidly. Typically, a turn where the price moves sharply away from the downward level can be considered a supply level. And conversely, a turning point where the price moves rapidly away from the level above can be considered a demand level.
When you find the turning point zone, grab a rectangular-shaped drawing object from your trading platform, and drag it to the right. Alternatively, there are some supply and demand trading indicators that are available in the market that you may be able to use.
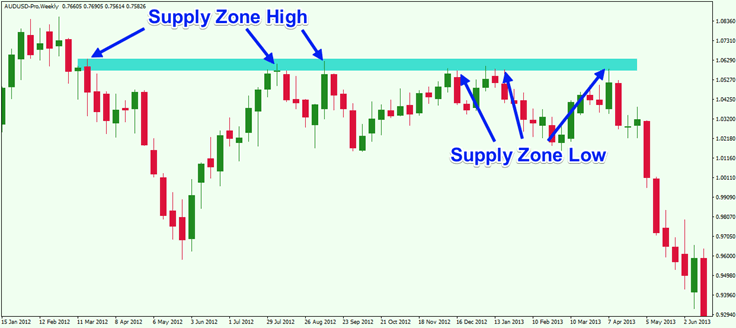
Above you will see a weekly chart of AUD/USD, which shows the supply level.
Supply and Demand Trading Strategies
Range Trading Strategy
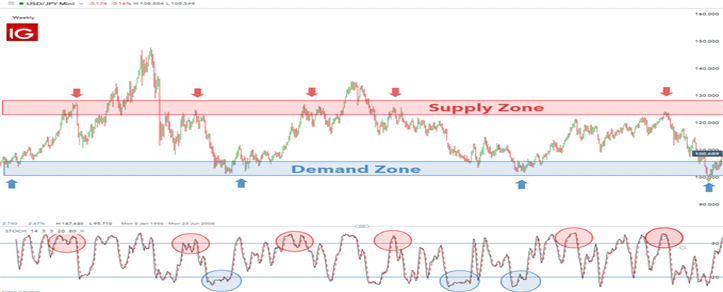
If the zones are well established, then supply and demand zones can be used for range trading. Traders may include using a stochastic indicator or RSI to help identify supply and demand overbought and oversold conditions.
Since this is a non-directional trade in terms of trend, both long and short entries can be seen. After viewing the oversold/overbought position on a long-term chart, traders can zoom in a shorter time frame to achieve an ideal entry.
Breakout Strategy
The breakout strategy is another supply and demand trading strategy. The value cannot remain within a defined range forever and will eventually make a directional movement. Traders want to get a favorable entry in the market towards a breakout, as this could be the beginning of a strong trend.
The USD/JPY chart exits the trading range but then returns to the demand zone. Traders holding a short trade in a breakout are likely to be closed in this scenario. One way to reduce this is to bring the retracement back into the demand zone before pacing short trades.
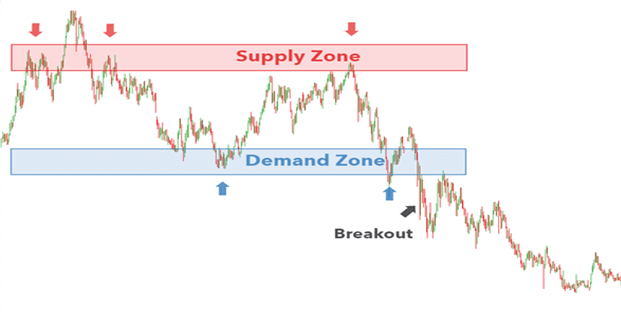
What are the Supply and Demand Zones?
Supply-demand nothing but the border area of support or resistance
Let analyze NIFTY 50 STOCK
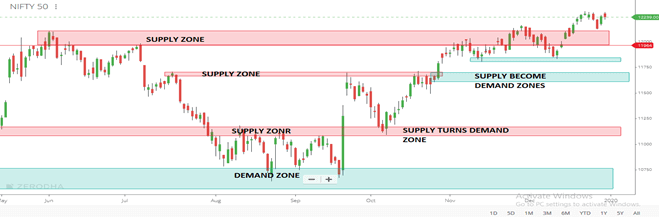
In the chart above, you can see a demand zone (broad support level) and a supply zone (a broad area of resistance).
What they want to find in value areas where supply increases demand and where demand increases supply.
- The former is known as the Super Zones. When the market hits SUPPLY ZONES, the price will decrease. Then, we can make money by shortening the market.
- The latter market is the demand zone. With the support of demand, price increases will occur. Then, we can gain in the long term.
- If the supply sector is broken, then it becomes a demand zone, pullback test from the demand zone we can go for a long time
The demand zone is a price zone below the current price action where there is strong buying interest. We can see that there was a lot of interest buying in the demand sector, most likely due to a large volume of buy orders at this level. For this reason, when the price reaches the level of demand, orders are executed, and a certain portion of the pending order volume is absorbed.
The supply zone is the exact opposite of the demand zone. A supply sector is located above the price action and typically has a relatively large volume of sales orders. When the price action reaches this level, the orders start executing.
Examples of Supply and Demand Forex
The two everyday examples of supply and demand Forex Trader in action are first in Australia with strawberry prices. When there was a bumper crop for the year, there was a large amount in return.
This forced strawberry prices to prices they had not traded in 10 years due to heavy oversupply in berries. Being largely larger than the demand for berries, this meant that most farmers had to adjust their prices accordingly (lowering them) to see any sales. Thus supply and demand affect the price.
Compare that when cyclones came through and drove out most of the banana crops. With the huge amount of banana crops that year, this meant that there was a huge supply of bananas in the market. People still wanted their bananas, and this created a balance in the market.
Because there was such a huge demand now, but a small supply, the price exceeded their normal prices at that low point of time by 10 x, which is a clear example of supply and demand for action.
It is also the trade supply and demand for action along with everyday goods that how supply and demand control prices in the forex markets. As bananas are priced higher, people move into their “panic” mode, and they start filling their shopping trolleys and creating more demand.
As others saw this crowd, they did so, and demand strengthened, and the price went up as well. The very principles in markets come into play with very human behaviors and mistakes, and that is why price action is so good for analyzing markets.
Japan Is the Example
We will provide an example of oil prices to explain how supply and demand zones work together and affect the global economy. If the demand for crude oil increases or the supply of crude oil decreases, the oil futures prices will usually increase. As crude oil prices rise, gasoline prices react almost immediately and rise simultaneously. As gasoline prices rise, consumers are forced to spend large amounts of money to drive themselves, say, point A to point B. And as they spend increasing amounts on oil-based products, they ultimately have less money than ever before the rise in oil prices. It is useful to mention that these factors, which affect an individual’s budget, also affect the budgets of the most well-known corporations and influential governments worldwide.
Let us take Japan as a country which suffers from high oil prices, as it imports almost all the oil. This means that Japan needs every barrel of oil to develop its industry; it must be purchased at some cost. In addition, the Japanese economy is dependent on its ability to export manufactured goods to its trading partners, such as the United States and China. As oil prices rise, every car, smartphone, and computer produced in Japan are increasingly spending money to distribute to consumers. In this case, the country experiences a double strike. First, he needs to import 100 percent of his oil at inflated prices, and then he needs to pay inflated prices to distribute 100 percent of the goods produced.
As a result of all this, Japanese goods will appear to be priced higher and fewer people will be able to afford them. The demand for the Japanese yen will decrease because the fewer items people buy, the less Japanese yen they need. The combination of increasing supply and decreasing demand will result in the devaluation of the Japanese currency.
Conclusion: Supply and Demand Foreign Exchange
Supply and demand trading techniques have great advantages using support and resistance levels. It can be traded as “set and forgotten” with pending orders. You know all trading prices (entry, stop loss, take-profit) ahead of time, and it provides a great RRR (Return-Risk Ratio).
However, like all techniques, it must be practiced and mastered. There are many caveats to be aware of. It takes time to learn how to handle them all. They recommend us to learn more and understand that it is not as simple as it sounds, nor is it a pure systematic strategy. This requires intensive learning.